Overview
English | 简体中文
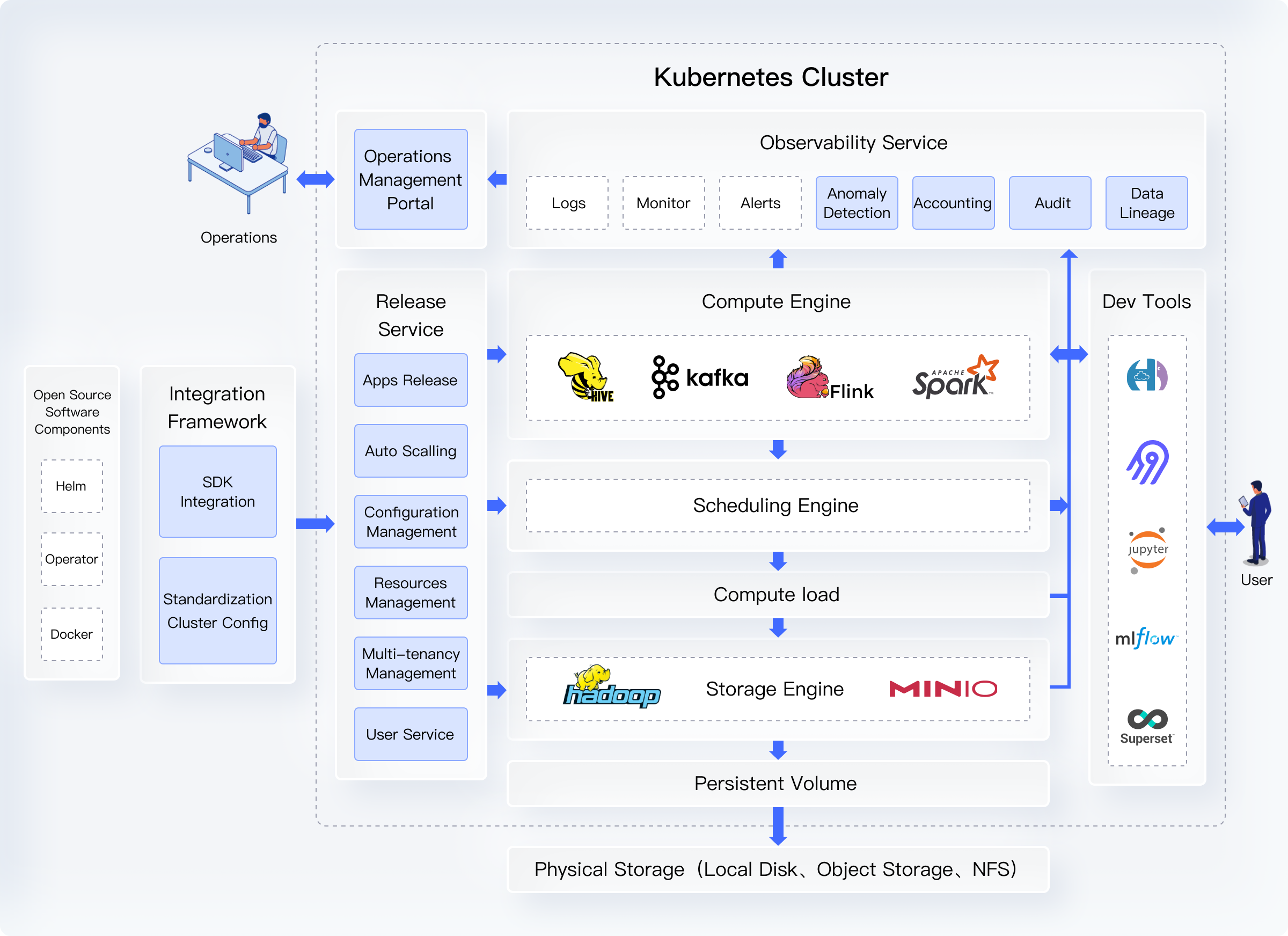
KDP(Kubernetes Data Platform) delivers a modern, hybrid and cloud-native data platform based on Kubernetes. It leverages the cloud-native capabilities of Kubernetes to manage data platform effectively.
Architecture
Advantages
- More efficient big data cluster management: KDP simplifies the operation and maintenance of big data clusters through standardized processes, and provides a UI interface to further improve the efficiency of deployment, upgrade and other operations
- More efficient integration of big data components: KDP provides standardized and automated deployment and operation of big data components, greatly reducing the development and online time of big data projects
- Higher cluster resource utilization: Compared with about 30% resource utilization of traditional big data platforms, KDP can be significantly increased to more than 60%
Highlights
- Unified Application release and management process based on OAM(Open Application Model) standard, open configuration management between components, and the implementation of IaC(Infra as Code)
- A unified abstraction layer is created on top of the Operator and Helm Chart of big data components to achieve standardization and automation of publishing and operation
- Code-level transformation of big data core components to support K8s resource scheduling, networking, and storage architecture, and unified integration of the latest versions of these components
- Using the K8s namespace to achieve multi-tenant management, resource isolation, on-demand dynamic resource allocation, and resource usage statistics and accounting components (Enterprise Edition)
- Extended and strengthened security authentication and authentication mechanisms in multi-tenant environments, using unified Kerberos security authentication and Ranger-based authorization mechanisms (Enterprise Edition)
- Optimized the performance of the computing engine in the cloud native form, such as: unified Volcano scheduling for batch/streaming jobs, solved the Data Locality problem of Spark on HDFS (enterprise edition)
Integration Framework
The KDP infrastructure layer provides a standard integration process based on the Open Application Model (OAM) to connect open source big data components with unified system services to form a standardized configuration file. Provides packaging based on the K8s configuration, simplifies the configuration process of big data components, and standardizes the docking mechanism between components and system services and other components. Mainly including:
- Provides flexible publishing configuration management, allowing users to specify big data cluster (underlying carrier is namespace) publishing, as well as dependent component specification
- If there are dependent external systems, the dependent system access address and configuration can be read from the system variables without hard coding
- Standardize how system configuration components such as ConfigMap/Secret are published and configured
- Provide log, monitoring, alarm and other operation and maintenance plug-in configuration, hide the underlying system details, automation, simplified configuration
- System configuration version management, comparison, rollback and other functions
Deployment Service
The KDP infrastructure layer provides a set of application publishing services that are responsible for publishing, updating, operating, and upgrading big data components from configuration files to K8s clusters. The biggest difference from the general PaaS platform is the integration of big data load support, tenant system, user management, and its resource management (the last three are Enterprise Edition features). Mainly including:
- Implement IaC(Infra as Code) release operation and maintenance mode, all operations in the way of modifying configuration files and in the way of Control Loop
- Take care of the publishing process between dependent components without manual handling
- Integration of system components and tenant systems to ensure that authorization, authentication, and warrant issuance are done in a cloud-native manner (Enterprise Edition)
- Management of tenants, lifecycle management of organizations/users and their associated resources (Enterprise Edition)
- Dynamic capacity expansion and reduction based on operating load (Enterprise Edition)
Observability
KDP provides big data components and their execution of workload logging, performance/stability metrics monitoring and alerting, billing, and auditing capabilities (enterprise features). The biggest difference from the generic PaaS platform is its support for run-to-finish jobs, second-level scheduling jobs, and data-level observability insights. Mainly including:
- Logging: Standardize log output for all components, including batch/streaming jobs
- Monitoring: Configure core O&M indicators of components and the collection mode. For batch/streaming jobs, push indicators need to be collected
- Alarming: Set reasonable alarm conditions and priorities according to indicators
- Anomaly detection: Automatically detect anomalies according to operation and maintenance indicators (Enterprise Edition)
- Billing: Requires a dedicated billing system to support both long-distance service and batch/streaming jobs (Enterprise edition)
- Auditing: Unified scheduling and operation and maintenance operation interface, and access to the audit system (Enterprise edition)
Scheduling service
KDP provides cloud-native scheduling mechanisms for computing engine components to improve resource utilization and operation efficiency. Based on the general K8s scheduling mechanism, the second level scheduling can better support the efficiency and SLA requirements of big data type loads. Mainly including:
- Supports scheduling of a large number of batch/streaming jobs
- Support for tenant isolation and elastic resource allocation (Enterprise Edition)
- Support for Data Locality (Enterprise Edition) in cloud-native environments
- Support intelligent and automated resource parameter Settings (Enterprise Edition)
- Supports different preemption and priority strategies (Enterprise Edition)
- Interface with existing tools to meet SLAs and resource usage requirements (Enterprise Edition)
Compute and storage engine
| Component | Notes |
|---|---|
| HDFS | * Extends Helm Chart for the open source community * Supports dynamic PV, container network and component context configuration management |
| Hive | * Extends the open source code to support Hive SQL running as Spark jobs * Supports running Hive SQL on a Hue or Beeline client * Hive tables can be stored in HDFS or object storage |
| Spark | * Extends Spark Operator from the open source community * Run Spark jobs via the self-developed API or JupyterLab * Extends open source code for performance optimization: Data Locality in HDFS, Sticky Sessions |
| Kafka | * Extends Strimzi Kafka Operator from the open source community * Integrates the Kafka cluster management web UI |
| Flink | * Extends Flink Operator from the open source community * Supports unified scheduling of Flink and Spark jobs |
| ... | ... |
